OpenAI Bolsters ChatGPT Security Against Sneaky Prompt Attacks
OpenAI Tightens ChatGPT's Defenses Against Crafty Hackers
ChatGPT just got tougher to trick. OpenAI announced significant upgrades to its AI's security system this week, specifically designed to thwart increasingly sophisticated prompt injection attacks - the digital equivalent of social engineering scams targeting artificial intelligence.
Locking Down Vulnerabilities
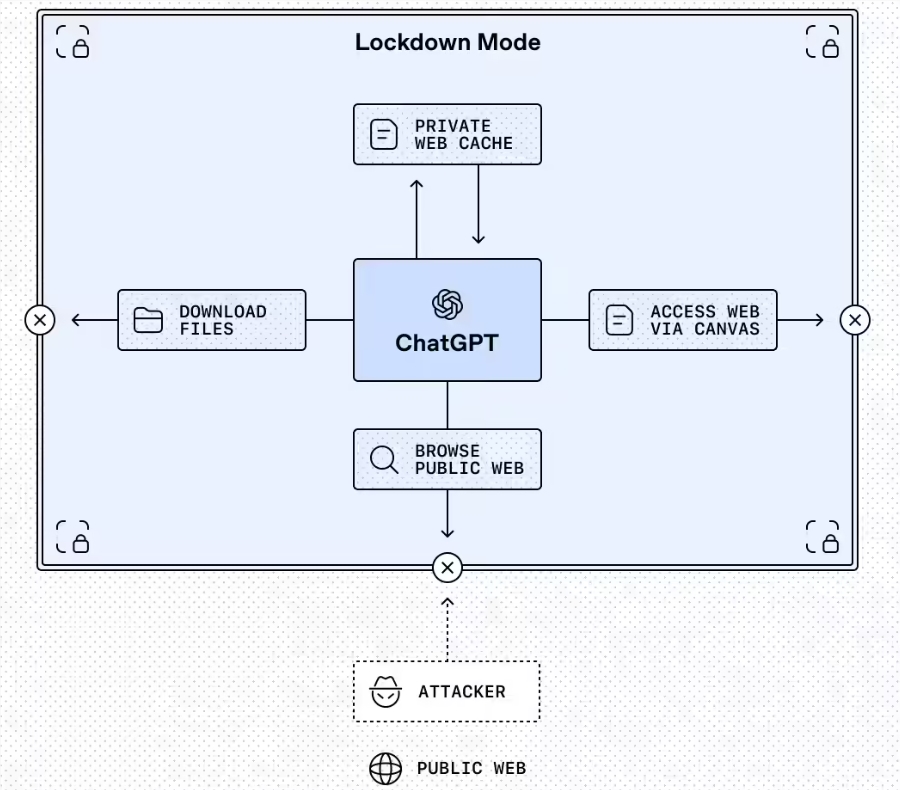
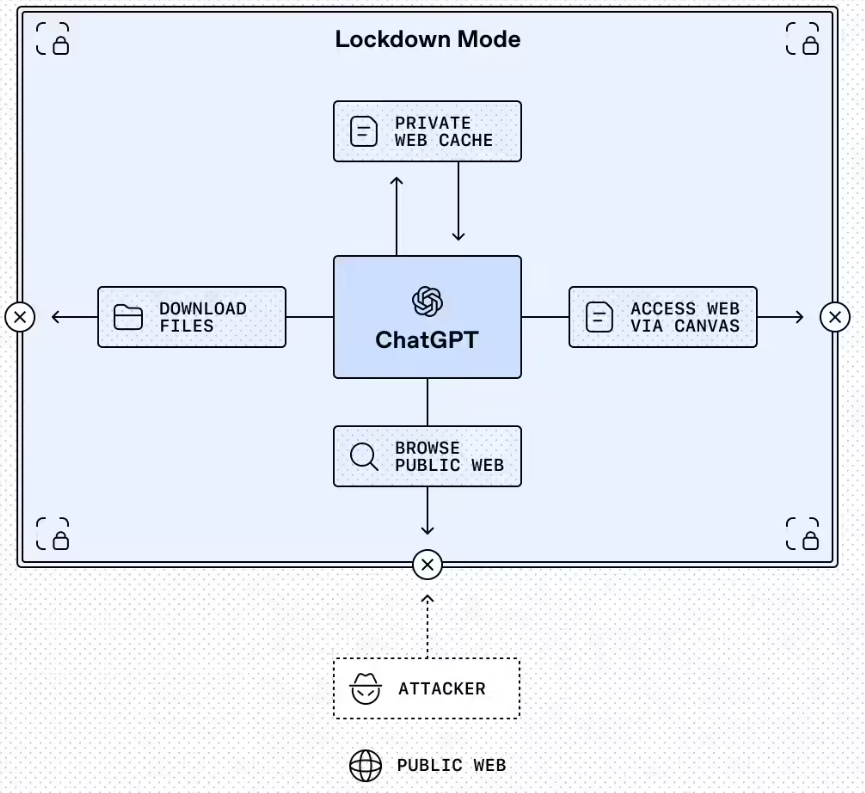
The standout feature is Lockdown Mode, an optional setting currently available for enterprise and education versions. Picture it as ChatGPT's version of putting on armor before entering sketchy neighborhoods online. When activated, it severely limits how the AI interacts with external systems:
- Web browsing gets restricted to cached content only
- Features without robust security guarantees get automatically disabled
- Administrators can fine-tune exactly which external applications remain accessible
"We're giving organizations tighter control over their risk exposure," explained an OpenAI spokesperson. "Lockdown Mode isn't meant for everyday chatting - it's digital body armor for high-stakes professional environments."
The mode arrives alongside enhanced dashboard controls letting IT teams:
- Create custom permission roles
- Monitor usage through Compliance API Logs
- Prepare detailed regulatory audits
Clear Warning Labels
The second major change introduces standardized "Elevated Risk" tags across ChatGPT, Atlas and Codex products. These bright red flags appear whenever users enable potentially dicey functions like unrestricted web access.
The labels don't just scream "danger!" - they provide practical guidance:
- Specific risks involved
- Recommended mitigation strategies
- Ideal use case scenarios
Developers working with Codex will especially appreciate these warnings when enabling network capabilities that could expose sensitive data.
Why This Matters Now
Prompt injection attacks have emerged as one of AI's most insidious threats. Clever hackers can manipulate chatbots into:
- Revealing confidential information
- Executing unauthorized commands
- Bypassing ethical safeguards
The new protections acknowledge that while internet-connected AI offers tremendous utility, those benefits come with real dangers that require thoughtful safeguards.
Looking ahead, OpenAI plans to bring Lockdown Mode to consumer versions within months - though most home users probably won't need its strictest settings.
Key Points:
- Lockdown Mode restricts risky external interactions for enterprise/education users
- Elevated Risk tags clearly warn about potentially dangerous functions
- Both features build on existing sandbox and URL protection systems
- Consumer version updates expected later this year