Gemini Under Siege: How Hackers Are Stealing AI Secrets
Google Sounds Alarm Over AI Model Theft
Security teams at Google are scrambling to protect their flagship Gemini AI system after discovering sophisticated attempts to steal its intellectual property. Attackers have been flooding the chatbot with massive volumes of queries - sometimes exceeding 100,000 prompts in a single attack - probing for weaknesses that reveal how the system thinks.
The Anatomy of an AI Heist
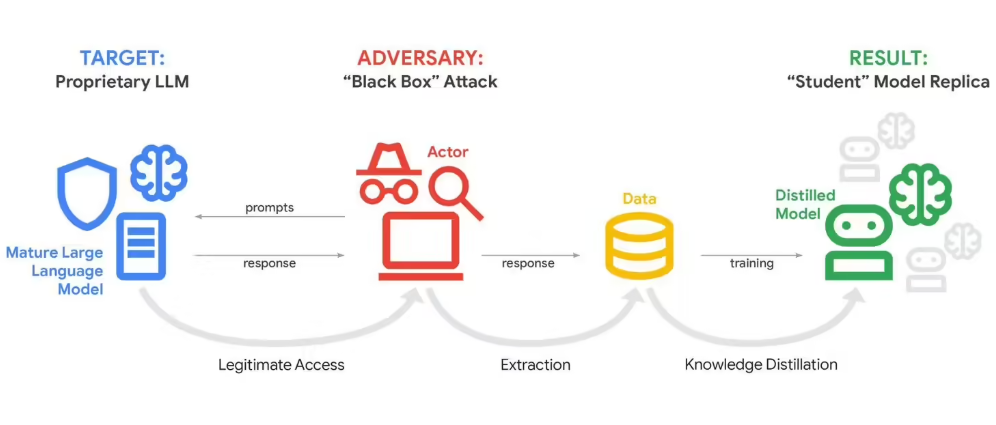
These so-called "model distillation attacks" work like digital pickpocketing. By analyzing thousands of responses, attackers can gradually piece together Gemini's internal reasoning patterns. "It's like someone repeatedly testing every combination on a safe," explains John Hottelquist, Google's threat intelligence chief. "Eventually, they'll hear the click."
The perpetrators appear to be commercial rivals rather than hobbyists or academics. Google reports detecting attack patterns consistent with professional AI development teams seeking shortcuts to build competitive systems.
Ripple Effects Across Industries
What makes this particularly troubling is its potential to spread beyond tech giants. As more businesses develop proprietary AI models containing sensitive data - from legal research tools to medical diagnostics systems - they become attractive targets for similar attacks.
Hottelquist draws parallels to early cybersecurity threats: "We're seeing warning signs today that could become tomorrow's epidemic." The concern isn't just about copied algorithms; attackers could extract years' worth of business insights embedded in these trained models.
Can This Be Stopped?
The challenge lies in balancing security with functionality. Unlike traditional software that can operate behind firewalls, large language models need open interfaces to be useful. Current detection systems can spot unusual query patterns, but determined attackers find ways around them.
"This isn't just a Google problem," emphasizes Hottelquist. "Every company investing in AI needs to think about protecting their digital crown jewels."
Key Points:
- Unprecedented scale: Attacks involve 100K+ prompts probing system logic
- Commercial motives: Competitors seek to replicate Gemini's capabilities
- Wider implications: Technique threatens corporate AI investments across sectors
- Security dilemma: Open access conflicts with IP protection needs