SenseTime's New AI Model Outperforms GPT-5 in Spatial Intelligence
SenseTime Breaks New Ground with Spatial Intelligence AI
In a move that could reshape how artificial intelligence interacts with physical spaces, Chinese tech giant SenseTime has launched its SenseNova-SI model series - and the results are turning heads across the industry. These open-source models aren't just keeping pace with global leaders; they're setting new benchmarks.
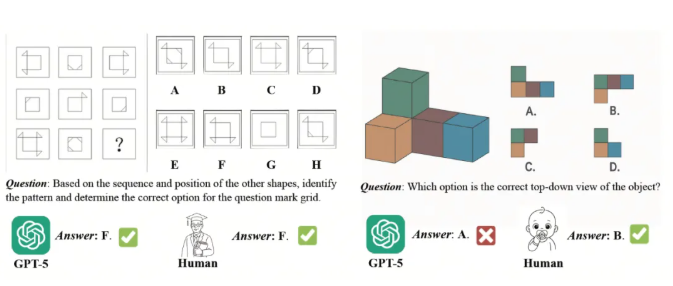
Closing the Spatial Gap
While current AI models excel at language tasks and logical reasoning, they've consistently struggled with spatial understanding - that crucial ability to comprehend and navigate three-dimensional environments. "We recognized this as a fundamental limitation," explains Dr. Li Wei, SenseTime's lead researcher on the project. "True embodied intelligence needs to understand space as humans do."
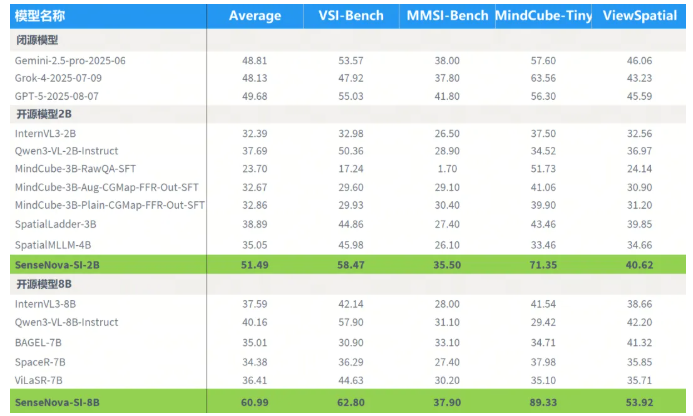
The solution? A systematic training approach leveraging massive datasets specifically designed to enhance spatial cognition. The results speak for themselves: the flagship SenseNova-SI-8B model achieved an impressive 60.99 average score on spatial intelligence benchmarks, outperforming both open-source competitors like Qwen3-VL-8B and proprietary systems including OpenAI's GPT-5.
More Than Just Numbers
What makes this breakthrough particularly noteworthy isn't just the superior performance metrics - it's how SenseTime achieved them. Their methodology focuses on six core aspects of spatial intelligence:
- Measurement: Precise distance and size estimation
- Reconstruction: Building mental models of environments
- Relationships: Understanding how objects interact spatially
- Perspective: Interpreting scenes from different viewpoints
- Deformation: Recognizing altered or distorted spaces
- Reasoning: Drawing logical conclusions about spatial arrangements
The implications extend far beyond academic benchmarks. Autonomous vehicles could navigate complex urban environments more safely. Robotics systems might manipulate objects with human-like precision. Even augmented reality applications could see dramatic improvements.
Setting New Standards
Alongside the model release, SenseTime introduced EASI (Evolutionary Assessment for Spatial Intelligence), an open evaluation platform designed to establish consistent metrics for measuring spatial understanding in AI systems.
The company has made both their models and evaluation tools publicly available through GitHub (https://github.com/EvolvingLMMs-Lab/EASI), signaling a commitment to advancing the field collectively rather than through proprietary silos.
The rapid progress suggests we may be approaching a tipping point where AI systems can understand and interact with physical spaces nearly as well as they process language - potentially opening doors to applications we've only begun to imagine.