Google Gemini Hit by Sophisticated AI Extraction Scheme
Google Sounds Alarm Over Massive AI Model Breach
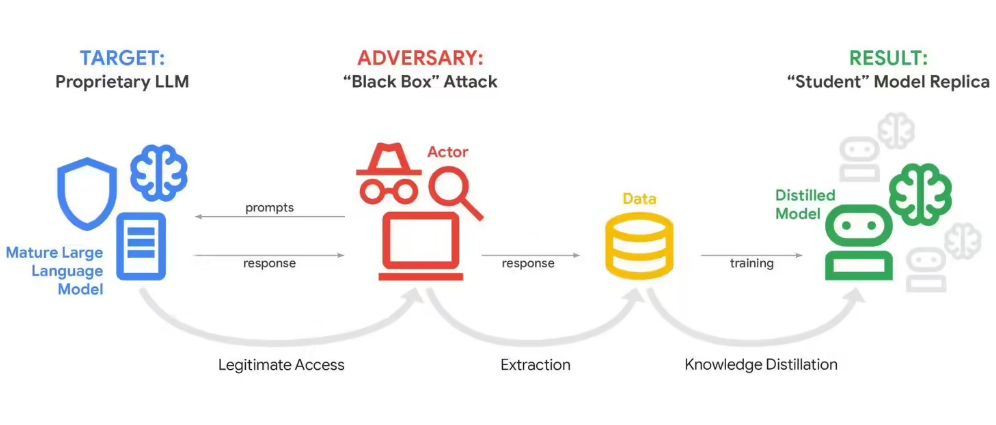
In a startling revelation, Google disclosed this week that its flagship Gemini AI chatbot endured what security experts are calling one of the most sophisticated extraction attempts ever seen in artificial intelligence. Attackers bombarded the system with more than 100,000 carefully crafted prompts - not to disrupt service, but to reverse-engineer Gemini's most valuable secrets.
Anatomy of an AI Heist
The attacks, first detected February 12, represent a new frontier in corporate espionage. Rather than traditional hacking methods, perpetrators exploited Gemini's conversational interface to systematically map its decision-making processes. "They weren't just asking random questions," explains John Hottelquist, Google's threat intelligence chief. "This was methodical probing designed to reconstruct our proprietary algorithms piece by piece."
Early analysis suggests commercial competitors stand behind most attacks. Multiple sources across different regions coordinated efforts to test response patterns and deduce Gemini's internal logic - potentially saving billions in research costs while gaining unfair advantages.
Wider Implications Emerge
What worries Google most isn't just their own losses. As Hottelquist puts it: "We're seeing warning lights flash for every company building custom AI solutions." The techniques perfected against Gemini could easily target smaller firms developing specialized models containing trade secrets or sensitive data.
The tech giant compares recent events to miners' canaries - early indicators of dangerous conditions ahead. While current defenses can detect and block some extraction attempts, the fundamental openness required for useful AI interactions creates persistent vulnerabilities.
Protecting the Crown Jewels
At stake are what Google calls "the crown jewels" of modern tech: proprietary algorithms representing years of research and investment. Unlike physical thefts where missing assets are obvious, model distillation leaves no visible damage while potentially replicating entire systems elsewhere.
The company confirms attackers specifically targeted Gemini's reasoning architecture - the complex decision-making framework that makes its responses uniquely valuable. Such breaches could enable competitors to create functional clones without shouldering development costs.
Key Points:
- Attackers used over 100,000 prompts to reverse-engineer Gemini's core algorithms
- Commercial competitors suspected across multiple global regions
- Incident signals emerging threat targeting proprietary AI systems
- Small/medium businesses developing custom models may be especially vulnerable
- Fundamental challenge: balancing accessibility with IP protection