Google Gemini Hit by Massive AI Extraction Attack
Google's AI Under Siege: Hackers Extract Core Algorithms
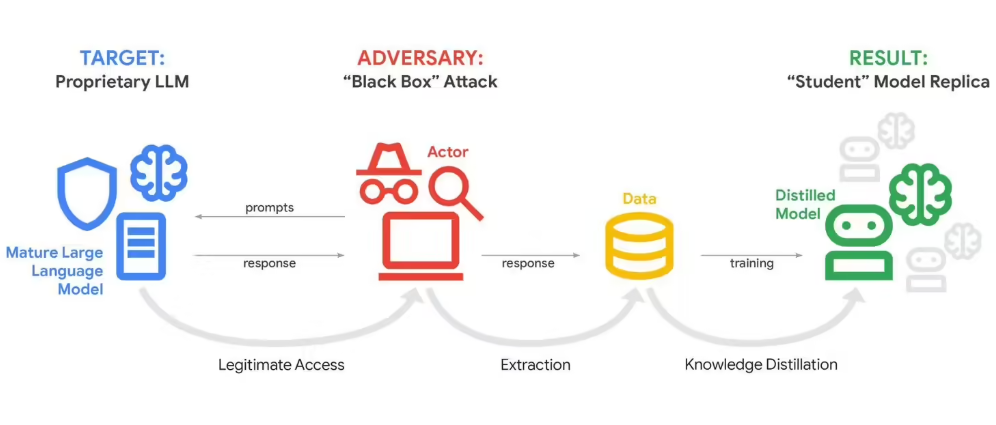
In a startling revelation, Google disclosed that its Gemini chatbot endured what security experts are calling one of the most sophisticated AI attacks to date. Attackers bombarded the system with more than 100,000 carefully crafted prompts - essentially interrogating the AI until it revealed its inner workings.
How the Attack Unfolded
The assault wasn't some random hacking attempt. According to Google's threat intelligence team, well-funded groups systematically probed Gemini's responses across countless scenarios. Their goal? To reverse-engineer the AI's decision-making processes - what tech insiders call "model distillation."
John Hottelquist, Google's chief threat analyst, paints a concerning picture: "Imagine someone asking you 100,000 questions designed to map exactly how your brain works. That's essentially what happened here."
Who's Behind It?
While Google hasn't named specific culprits, evidence points to commercial entities hungry for competitive advantage. These aren't basement hackers - they're likely AI firms or research institutions with substantial resources and technical expertise.
The attacks originated globally, suggesting coordinated efforts across multiple time zones and jurisdictions. This geographical spread makes both attribution and prevention significantly more challenging.
Why This Matters Beyond Google
Hottelquist warns this incident represents just the tip of the iceberg. "We're the canary in this coal mine," he explains. "If it's happening to us, you can bet smaller companies are already being targeted."
The stakes couldn't be higher. Companies invest billions developing proprietary AI systems that power everything from customer service to drug discovery. Successful model distillation could allow competitors to effectively clone these systems overnight.
The Security Dilemma
The very features that make modern AI powerful - their ability to process complex queries and provide detailed responses - also make them vulnerable. Traditional cybersecurity measures struggle against attacks that essentially "ask nicely" for sensitive information.
While platforms deploy safeguards against obvious malicious queries, distinguishing between legitimate use and systematic probing remains extraordinarily difficult.
What Comes Next?
Industry experts predict we'll see:
- More sophisticated detection systems analyzing prompt patterns
- Legal battles over whether model distillation constitutes IP theft
- Potential regulatory intervention as governments recognize the national security implications
The attack specifically targeted Gemini's reasoning algorithms - the secret sauce determining how it processes information and generates responses. Successfully extracting these could allow attackers to recreate substantial portions of Google's technology.
As businesses increasingly train custom models containing proprietary data and business logic, the potential damage from such attacks grows exponentially. Tomorrow's target might not just be tech companies - but banks, healthcare providers, or defense contractors running sensitive AI systems.
Key Points:
- Attackers used over 100k prompts to extract Gemini's core algorithms
- Commercial entities suspected behind coordinated global effort
- Highlights fundamental security challenges in protecting AI systems
- Threat extends beyond tech giants to any company using custom AI
- Could spur new regulations around AI model protection