Google's Gemini AI Under Siege: Hackers Extract Secrets Through 100,000+ Questions
Google's Gemini AI Faces Unprecedented Security Breach
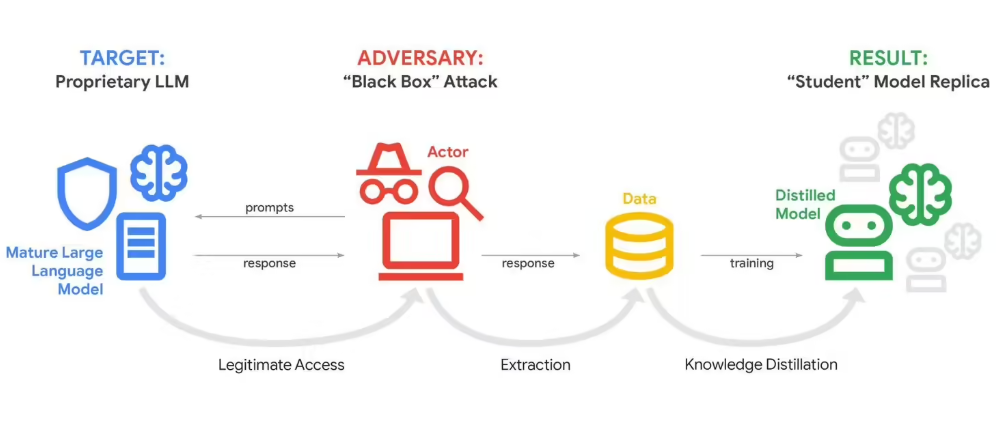
In a startling revelation, Google disclosed that its flagship Gemini AI chatbot has been targeted by what security experts are calling the largest-scale "model distillation attack" to date. Attackers flooded the system with more than 100,000 carefully crafted prompts in attempts to reverse-engineer its core algorithms.
How the Attack Unfolded
The assault, detected on February 12, represents a new frontier in AI security threats. Rather than traditional hacking methods, perpetrators used the chatbot's own interface as a weapon. By analyzing patterns in Gemini's responses to thousands of variations of similar questions, attackers could piece together how the AI makes decisions - essentially stealing its "thought process."
"This isn't just about one company's security," warned John Hottelquist, Google's chief threat analyst. "We're seeing the first waves of what could become an industry-wide crisis for AI developers." The tech giant believes commercial competitors are behind most attacks, though they declined to name specific organizations.
Why This Matters for Businesses
At stake are billions in research investments. Major tech firms pour enormous resources into developing unique AI architectures that power their chatbots. These proprietary systems represent competitive advantages that companies fiercely protect.
The attacks expose a fundamental vulnerability: the very openness that makes AI assistants useful also makes them vulnerable. "It's like having a brilliant employee who can't help but explain exactly how they solve every problem," explained one security researcher who requested anonymity.
The Growing Threat Landscape
What began as academic curiosity about how AIs work has evolved into sophisticated corporate espionage. Smaller companies developing specialized AI tools may be especially vulnerable. Without Google-scale security teams, they could lose valuable intellectual property before even realizing they're under attack.
Hottelquist draws parallels to early internet security challenges: "We're at that moment where everyone recognizes there's danger, but we haven't yet developed the right protections."
Key Points:
- Unprecedented Scale: Over 100,000 prompts used in single attack instances
- Commercial Motives: Competitors likely seeking to replicate Google's AI advancements
- Industry-Wide Risk: Attack method could target any company using large language models
- Protection Challenges: Current defenses struggle against this novel attack vector
- Future Concerns: Potential for extraction of sensitive business data from customized AIs