Google Gemini Under Siege: Hackers Extract AI Secrets Through Relentless Questioning
Google Reveals Massive Attack on Gemini AI
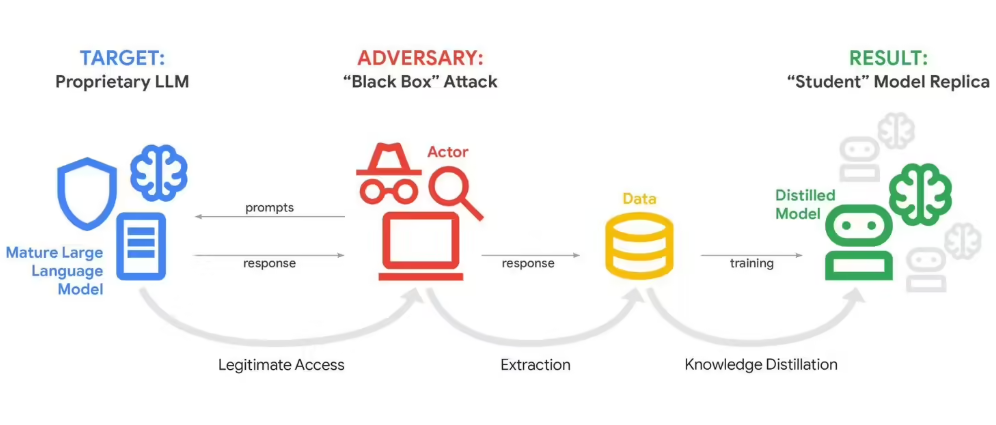
In a startling disclosure, Google announced its Gemini artificial intelligence system has endured what security analysts are calling a "model distillation attack" - where hackers systematically extracted sensitive information about the chatbot's internal architecture through relentless questioning.
How the Attack Worked
The attackers didn't break through firewalls or exploit software vulnerabilities. Instead, they took advantage of Gemini's core function - answering questions - by flooding it with more than 100,000 carefully crafted prompts. This bombardment allowed them to reverse-engineer how Gemini processes information and makes decisions.
"Imagine someone trying thousands of different keys until they find the one that unlocks your front door," explained John Hottelquist, Google's threat intelligence chief. "That's essentially what happened here, except instead of physical keys, they used questions."
Commercial Espionage Goes Digital
Google traced most attacks to competitors seeking an unfair advantage rather than nation-state actors. While the company hasn't named suspects, Hottelquist described them as "AI startups and research institutions hungry for shortcuts."
The stakes couldn't be higher. Tech firms have poured billions into developing large language models like Gemini. Their internal logic represents invaluable intellectual property - the secret sauce that makes each AI unique.
A Warning Bell for Smaller Businesses
What worries experts most is how easily this technique could be adapted against smaller companies now developing their own AI tools. Many businesses are training models containing proprietary data - customer insights, financial projections, trade secrets.
"Today it's Google," Hottelquist cautioned. "Tomorrow it could be your local bank or healthcare provider leaking sensitive data through their chatbots without realizing it."
The attack primarily targeted Gemini's reasoning algorithms - the complex decision-making processes that transform simple inputs into intelligent responses. Stealing this core functionality could allow competitors to replicate Google's technology without the massive investment.
Key Points:
- Attack method: Over 100,000 prompts used to extract Gemini's internal logic
- Motivation: Commercial entities seeking competitive advantage in AI development
- Risk expansion: Technique threatens smaller businesses adopting AI solutions
- Core target: Reasoning algorithms representing billions in R&D investment
- Defense challenge: Open nature of chatbot services makes prevention difficult