China-Led Team Sets Global Standard for Trustworthy AI Agents
China Establishes Global Benchmark for AI Agent Security
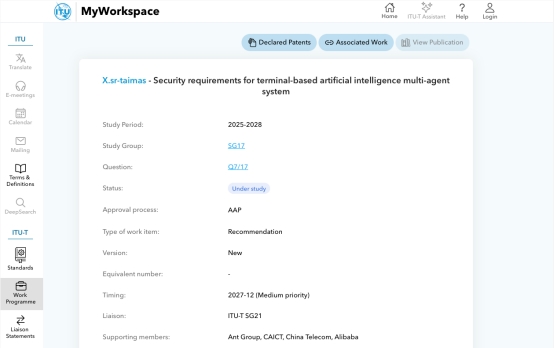
In a significant move for the AI industry, Chinese technology leaders have successfully established an international standard governing trustworthiness in multi-agent systems. The milestone achievement came during recent ITU-T meetings in Geneva, where experts unanimously approved the "Trusted Requirements for Terminal Multi-Agent Systems" proposal.
Building Trust in AI Interactions
The new standard tackles one of AI's most pressing challenges - how to ensure secure and reliable communication between intelligent agents across different platforms. "Imagine multiple digital assistants from various companies needing to collaborate," explains Deng Youjun from China Academy of Information and Communications Technology. "Without common security protocols, we're leaving doors open to attacks."
The framework focuses on four pillars:
- Trusted connection - Ensuring secure communication channels
- Trusted identity - Verifying who (or what) you're interacting with
- Trusted intent - Confirming instructions haven't been tampered with
- Trusted authorization - Properly managing access permissions
 (Caption: Visual representation of trusted multi-agent system interactions)
(Caption: Visual representation of trusted multi-agent system interactions)
From Open Source to Global Standard
The technology behind this standard originated from Ant Group's work with the Internet Trusted Authentication Alliance (IIFAA). Their open-source ASL technology - already proven in real-world applications - now forms the foundation of this international framework.
"This isn't just about technical specifications," notes an Ant Group representative present at the Geneva meetings. "We're creating the digital equivalent of traffic laws for AI agents - rules that allow different systems to interact safely regardless of who built them."
 (Caption: Delegates discussing standards at ITU-T SG17 meeting)
(Caption: Delegates discussing standards at ITU-T SG17 meeting)
Why This Matters Now
With generative AI accelerating agent adoption globally, security gaps have become increasingly apparent. Recent incidents have shown how malicious actors can exploit:
- Weak authentication between agents
- Unverified command transmissions
- Inadequate permission controls The new standard directly addresses these vulnerabilities.
The ITU endorsement carries particular weight as one of only three globally recognized standards bodies alongside ISO and IEC. Approval here means worldwide recognition and adoption potential.
The development team estimates about two years of refinement before final publication. During this period, they'll incorporate feedback from international stakeholders while maintaining backward compatibility with existing implementations like ASL.
Key Points:
- Global Recognition: First international standard establishing trust protocols for multi-agent systems
- Chinese Leadership: Spearheaded by Ant Group with CAICT and China Telecom
- Security Focus: Addresses connection, identity, intent and authorization risks
- Real-World Roots: Based on proven ASL technology already in use
- Ecosystem Impact: Expected to accelerate safe adoption of collaborative AI agents