GPT-5.2 Outshines Claude Opus in Marathon Coding Challenges
AI Coding Assistants Put to the Test
Cursor's recent benchmark tests reveal fascinating differences between today's top AI programming assistants. When tasked with building complex systems from scratch, OpenAI's GPT-5.2 showed remarkable endurance where competitors faltered.
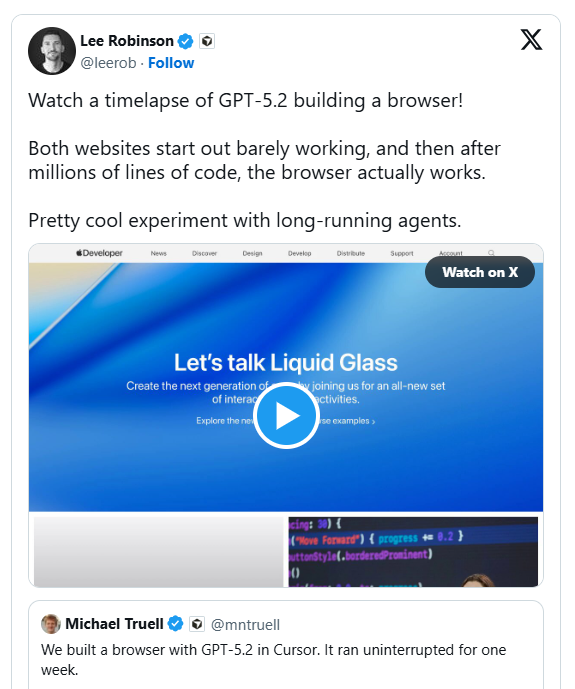
The development team created an ambitious stress test: constructing a complete web browser entirely through AI automation. This wasn't just surface-level coding - the challenge included fundamental components like HTML parsers, CSS layout engines, and even a custom JavaScript virtual machine.
"We wanted to see how these models would perform on projects requiring sustained focus over weeks," explained a Cursor spokesperson. "It's one thing to solve discrete problems, but maintaining context across millions of lines of code is entirely different."
Marathon vs Sprint Performance
GPT-5.2 consistently delivered coherent, on-target code throughout the extended development cycle. Unlike human programmers who might lose steam, the AI maintained steady progress without compromising quality or cutting corners.
Claude Opus4.5 started strong but struggled with long-term consistency. While excellent at solving individual problems, it occasionally lost sight of overarching goals or attempted premature completion of complex subsystems.
The differences became particularly apparent in:
- Maintaining architectural vision across months of development
- Handling intricate dependencies between components
- Resisting the temptation to simplify challenging requirements
The Rust-based browser kernel ultimately achieved impressive results, including rendering pipeline optimizations that boosted performance by 25x.
Beyond Browser Development
Cursor has since deployed GPT-5.2 for other ambitious projects:
- A fully functional Windows7 simulator
- Migration of legacy systems exceeding one million lines of code
- Automated implementation of sophisticated visual effects (smooth zooming, dynamic blur)
The implications extend far beyond programming assistance tools. These results suggest AI may soon undertake complete software projects independently - work that currently requires coordinated human teams.
Key Points:
- Endurance matters: GPT-5.2 demonstrates superior focus in extended coding sessions compared to Claude Opus4.5
- Real-world validation: The browser project proves AI can handle multi-component engineering challenges
- Performance gains: Automated optimization achieved 25x improvements in critical subsystems
- Expanding capabilities: Successful completion of Windows simulator shows breadth of application