GPT-4 Output Improves 20% with Self-Refine Method, No Training Required
A breakthrough in artificial intelligence has emerged with the Self-Refine method, demonstrating how large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 can significantly improve their own outputs without additional training. This innovative approach achieves approximately 20% better performance through autonomous self-criticism and iterative refinement.
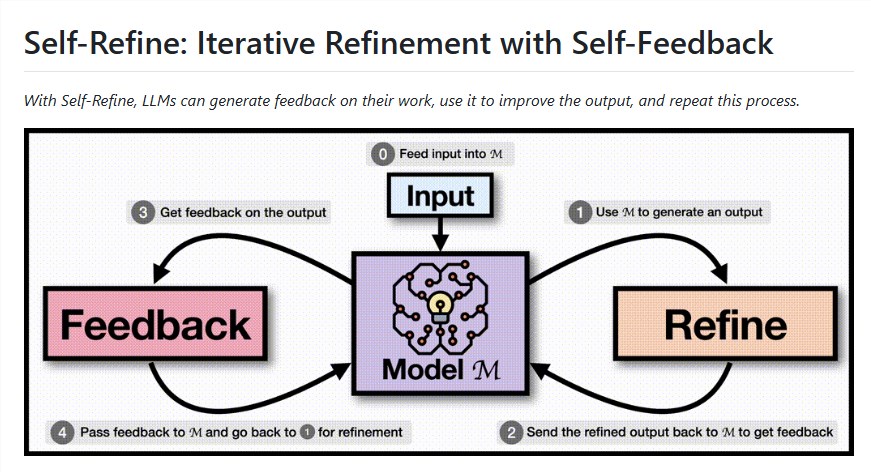
How Self-Refine Works The system operates through a three-step loop:
- Initial Response Generation: The model produces its first output based on input prompts
- Self-Evaluation: The AI critically assesses its own work, identifying areas for improvement
- Optimization: Using its feedback, the model refines the output until meeting quality standards
Researchers found this method particularly effective for advanced models like GPT-4, where it improved performance across seven different tasks by an average of 20%. In specific applications like code readability, improvements reached as high as 40%. What makes Self-Refine remarkable is its simplicity - it requires no new training data or external tools, just carefully designed prompts.
Practical Applications Show Promise The technique has demonstrated impressive results across multiple domains:
- Code Optimization: GPT-4's coding performance improved by 8.7 units with readability increasing 13.9 units
- Conversational AI: Initial dialogue outputs preferred by only 25% of humans rose to 75% after refinement
- Content Creation: Story generation saw quality improvements of 21.6 units in logical flow and appeal
The open-source availability of Self-Refine (https://github.com/ag-ui-protocol/ag-ui) has lowered barriers for developers to implement these improvements. However, the system does have limitations - weaker base models struggle to generate useful self-feedback, and the iterative process can increase computational costs.
Industry Context and Future Directions Self-Refine enters a competitive landscape of self-improving AI systems. Unlike methods relying on external tools or additional training data, this approach stands out for its simplicity and generality. Early adopters report particular value in resource-constrained environments where adding external components isn't feasible.
The technique represents an important step toward more autonomous AI systems capable of self-assessment and improvement. Future developments may expand Self-Refine to multimodal applications like image and voice generation, or combine it with other techniques like Chain-of-Thought reasoning.
As with any emerging technology, challenges remain in ensuring consistent feedback quality and managing computational overhead - especially for real-time applications. The open-source community continues working to refine these aspects while exploring new applications.
Key Points
- Self-Refine improves LLM outputs by ~20% without additional training
- The method works through generation-feedback-refinement cycles within a single model
- Best results appear with advanced models like GPT-4; weaker models struggle with self-feedback
- Applications range from code optimization to conversation and content creation
- Computational costs and feedback consistency remain key challenges