Google Gemini Under Siege: Hackers Extract AI Secrets Through Relentless Questioning
Google Battles Massive Attack on Gemini AI
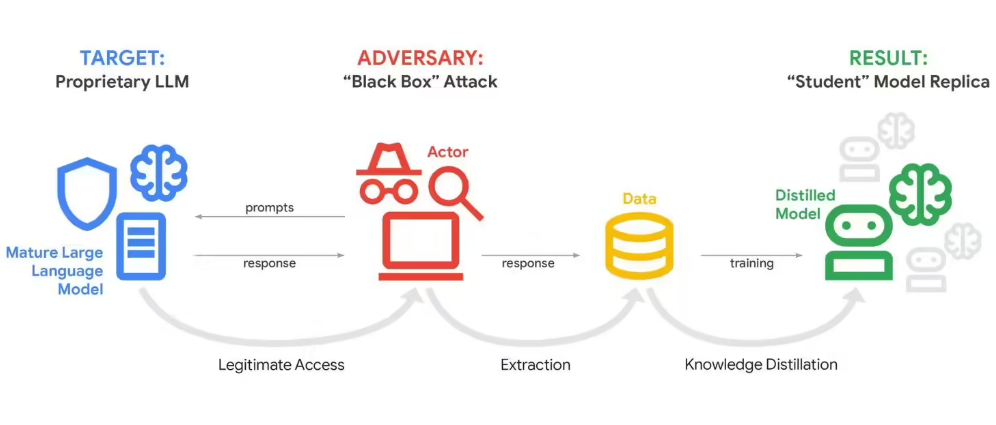
In what security experts are calling an unprecedented assault on artificial intelligence systems, Google disclosed this week that its Gemini chatbot has been subjected to a relentless barrage of questioning designed to extract its core algorithms. Attackers have been flooding the system with carefully crafted prompts - sometimes exceeding 100,000 queries in a single attack - attempting to reverse-engineer how the AI thinks.
The Anatomy of an AI Heist
The technique, known as "model distillation," works much like repeatedly interviewing someone to understand their decision-making process. By analyzing patterns in Gemini's responses across thousands of variations on similar questions, attackers can piece together the underlying logic that powers the AI.
"This isn't just curiosity - it's corporate espionage," said John Hottelquist, Google's chief threat analyst. "We're seeing well-funded groups systematically probing our systems, trying to steal what amounts to billions in research and development."
Who's Behind the Attacks?
While Google hasn't named specific culprits, evidence points to competing AI companies and research institutions looking for shortcuts in the race for artificial intelligence dominance. The attacks originate from multiple global locations, suggesting coordinated efforts rather than isolated incidents.
The stakes couldn't be higher. Large language models like Gemini represent some of tech companies' most valuable assets - products of massive investments in computing power and human expertise. Their inner workings constitute trade secrets comparable to Coca-Cola's famous formula.
A Warning Bell for All Businesses
Hottelquist describes Google's experience as "the canary in the coal mine" for AI security. As more businesses develop customized AI tools containing proprietary data and processes, they become potential targets for similar extraction attempts.
The attacks expose a fundamental tension in today's AI landscape: these powerful tools need broad accessibility to be useful, but that same openness makes them vulnerable. Current safeguards can detect and block many extraction attempts, but determined attackers willing to invest time and resources often find ways around them.
What This Means Going Forward
The revelation raises tough questions about balancing innovation with protection in the AI sector:
- How can companies safeguard their investments while keeping products accessible?
- Should there be legal consequences for model distillation attempts?
- Will this accelerate moves toward more closed-off AI systems?
One thing seems certain: as artificial intelligence becomes increasingly central to business operations worldwide, securing these systems will only grow more critical - and more challenging.
Key Points:
- Scale: Attacks involve over 100,000 prompts targeting Gemini's core logic
- Motivation: Commercial competitors seeking proprietary AI algorithms
- Risk: Potential theft of years worth of research and development investment
- Broader Impact: Signals emerging threats facing all businesses using custom AI