Gemini Under Siege: Hackers Extract AI Secrets Through Massive Prompt Attacks
Google Sounds Alarm Over AI Model Theft Scheme
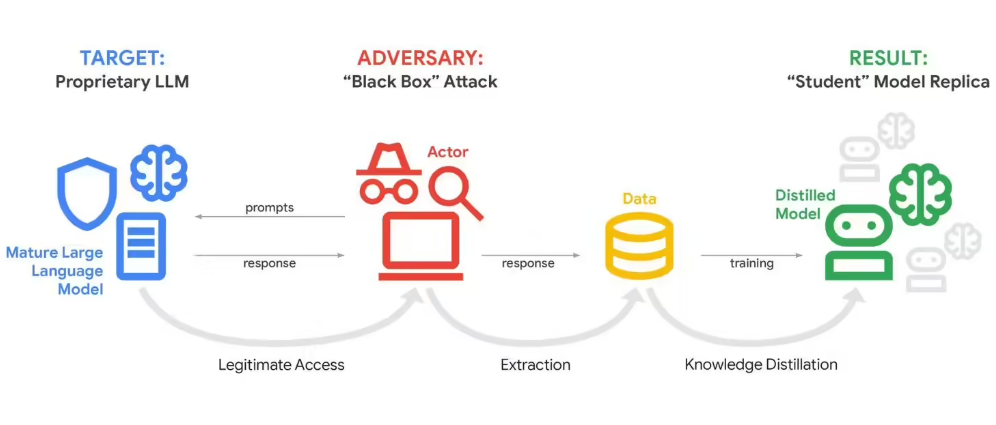
Security teams at Google have uncovered a disturbing trend - hackers are systematically probing Gemini's artificial intelligence through what experts call "model distillation attacks." Rather than traditional hacking methods, these assailants are exploiting the chatbot's very nature by flooding it with hundreds of thousands of carefully crafted prompts.
"Imagine someone asking you the same question 100 different ways," explains John Hottelquist, Google's threat intelligence chief. "Eventually patterns emerge that reveal how you think. That's essentially what's happening here, but at industrial scale."
The attacks first came to light February 12 when Google noticed unusual activity patterns targeting Gemini. Unlike typical users who might ask dozens or even hundreds of questions, these attackers were submitting tens of thousands of queries in systematic attempts to map out Gemini's internal logic.
The Corporate Espionage Angle
Behind these digital assaults appear to be well-funded organizations - likely competing AI firms or research institutions according to Google's investigation. Their goal? To either clone Gemini's capabilities or boost their own systems by reverse-engineering its algorithms.
"This isn't just academic curiosity," Hottelquist warns. "We're talking about potential theft of intellectual property worth billions in development costs."
The attacks originate from multiple global locations, though Google remains tight-lipped about specific suspects. What concerns security teams most is how this technique could proliferate.
A Warning Bell for AI Security
Google compares its experience to the proverbial canary in the coal mine - an early indicator of dangers facing the entire industry. As more companies develop proprietary AI models containing sensitive business data, they become potential targets for similar extraction attempts.
Current defenses struggle against these novel attacks because they exploit fundamental aspects of how large language models operate. While platforms can detect and block suspicious activity patterns, completely preventing such probing while maintaining useful functionality presents an ongoing challenge.
The attackers appear particularly focused on uncovering Gemini's reasoning algorithms - the secret sauce governing how it processes information and arrives at conclusions. Successfully extracting this could allow competitors to replicate key capabilities without investing in original research.
Key Points:
- Hackers using massive prompt volumes (100k+) to reverse-engineer Gemini's logic
- Attacks likely commercially motivated by rival firms/researchers
- Technique threatens core intellectual property worth billions
- Warns of broader risks as custom AI models proliferate
- Current defenses limited due to inherent model openness