ChatGPT's Split Personality: Why Its Web and API News Recommendations Differ
ChatGPT's Web and API Versions Tell Different News Stories
Ever noticed how ChatGPT seems to change its mind depending on how you access it? A groundbreaking study from the University of Hamburg and Leibniz Institute for Media Research reveals the AI assistant has a split personality when recommending news sources.
The Great Divide in News Recommendations
Over five weeks, researchers analyzed more than 24,000 ChatGPT responses to news-related queries from German users. What they found was striking: the web interface and API don't just differ slightly—they operate like separate news curators.
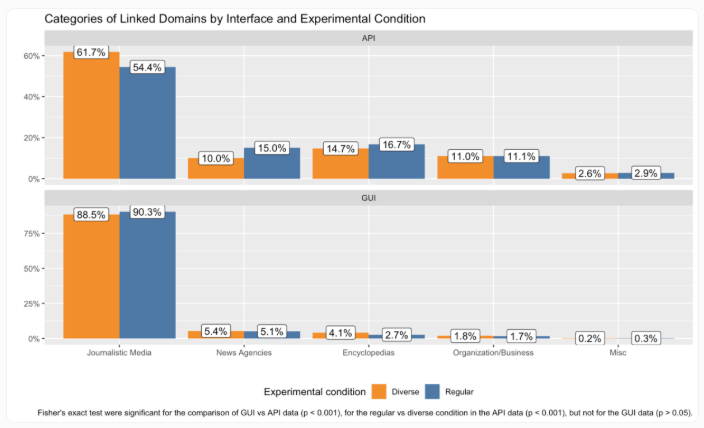
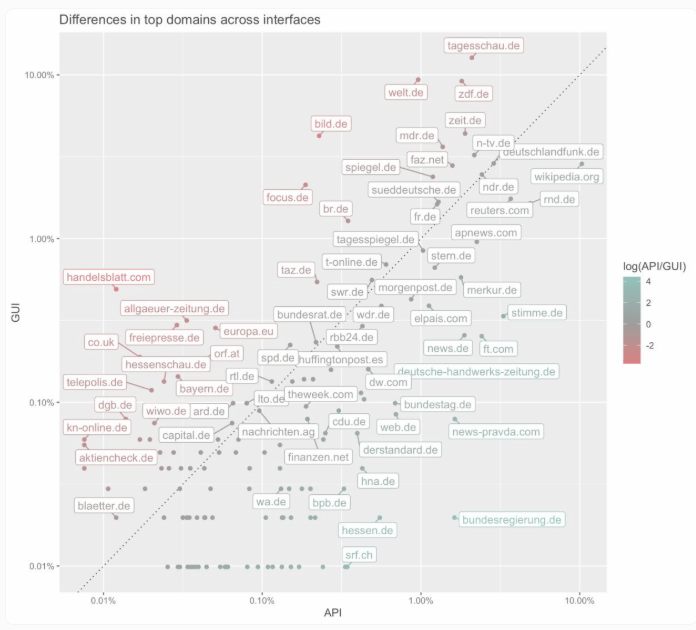
The web version plays it safe with mainstream media like tagesschau.de, while the API ventures into Wikipedia territory and obscure tech blogs. Conservative outlets like welt.de appeared 13% of the time in web responses but barely registered (2%) through the API.
"It's like getting recommendations from two different friends—one who reads the newspaper religiously, and another who gets all their information from random internet forums," noted one researcher.
Credibility vs. Diversity Dilemma
The study compared sources against the Reuters Digital News Report 2025, finding:
- Web interface: 45.5% overlap with established media
- API: Just 27.3% overlap
Public broadcasting outlets fared particularly well in web recommendations but got less love through the API. While both versions increased source diversity when prompted, quantity didn't always mean quality—some responses included politically biased sites or even non-existent domains.
The Transparency Problem
Here's what keeps researchers up at night: No one knows why these differences exist. OpenAI hasn't explained the discrepancy between interfaces, leaving users to wonder which version to trust. Compounding the issue, silent system updates mean today's findings might not hold true tomorrow.
"We're dealing with a black box that reshapes itself without warning," said lead researcher Dr. Elena Müller. "When an AI recommends different facts through different doors, that's not just curious—it's concerning."
The study highlights fundamental differences between generative AI and traditional search engines in how they process and present information—differences that could shape public understanding in unseen ways.
Key Points:
- Web interface favors mainstream media, API leans toward niche sources
- 45.5% vs. 27.3% overlap with reputable news outlets (web vs. API)
- Source diversity doesn't always equal reliability—some recommendations led to questionable sites
- OpenAI hasn't explained why these disparities exist
- System updates happen without notice, making results potentially temporary



