Microsoft Unveils Agent Lightning: AI Framework for LLM Training
Microsoft Launches AI Framework to Revolutionize LLM Training
Microsoft has unveiled Agent Lightning, a groundbreaking open-source framework that leverages reinforcement learning (RL) to optimize multi-agent systems for large language model (LLM) training. The innovative system captures real agent behavior and converts it into RL transitions while maintaining compatibility with existing architectures.
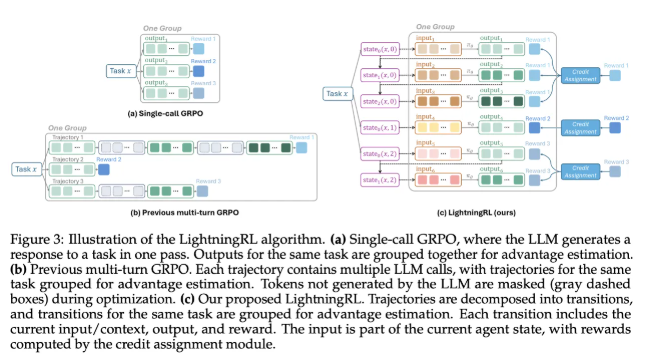
How Agent Lightning Works
The framework models agents as partially observable Markov decision processes, where:
- Observations represent current inputs
- Actions correspond to model calls
- Rewards include both terminal and intermediate values
Agent Lightning extracts call logs containing input, output, and reward data while filtering out noise to create clean transition datasets for training. This approach maintains the integrity of existing systems while significantly improving model performance.
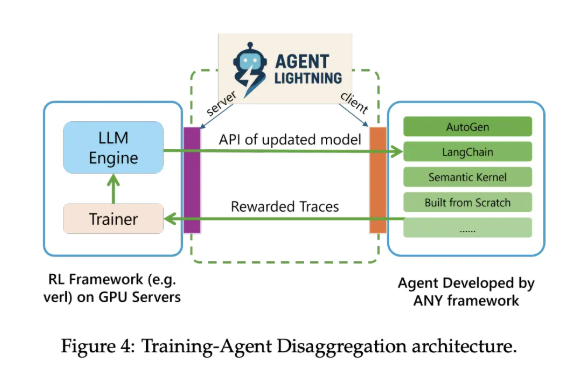
Decoupled Architecture Design
The system employs a novel "training and deployment decoupling" approach consisting of:
- Lightning Server: Handles training and service operations while providing OpenAI-compatible API interfaces
- Lightning Client: Captures runtime call logs and transmits data to the server in real-time
This architecture keeps GPU-intensive training on the server layer while maintaining seamless integration with tools and browsers.
Flexible Tracking Options
The framework offers two data collection pathways:
- OpenTelemetry integration for standardized telemetry collection
- Lightweight embedded tracker for teams preferring minimal infrastructure Both methods ultimately store data in unified locations for consistent training processes.
Performance Validation
Microsoft researchers tested Agent Lightning across three challenging benchmarks:
- Text-to-SQL: Achieved stable reward improvements on the Spider benchmark (10,000+ questions across 200 databases)
- Retrieval-augmented generation: Demonstrated effectiveness on MuSiQue benchmark (21 million Wikipedia-scale documents)
- Math QA: Showed significant gains on Calc X dataset through tool-based calculations
The complete research paper is available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.03680v1
Key Points
- 🚀 Open-source solution that enhances multi-agent systems without structural changes
- 🔍 Models agents as partially observable Markov decision processes for precise training
- ⚡ Decoupled architecture maintains system stability during updates
- 📈 Proven performance gains across text-to-SQL, retrieval, and math applications