Google AI Unveils DeepSomatic for Cancer Mutation Detection
Google AI Launches Breakthrough Cancer Detection Model
Google Research, in partnership with the University of California, Santa Cruz, has unveiled DeepSomatic, a cutting-edge artificial intelligence model designed to identify genetic mutations in cancer cells. The announcement comes after successful trials detecting pediatric leukemia mutations that conventional tools missed.
How DeepSomatic Works
The innovative model employs:
- A small variant caller specifically optimized for cancer genomes
- Compatibility with Illumina short reads, PacBio HiFi long reads, and Oxford Nanopore long reads
- An extension of Google's DeepVariant technology
The system converts aligned DNA reads into image-like tensors that encode:
- Base stacking information
- Quality metrics
- Alignment context
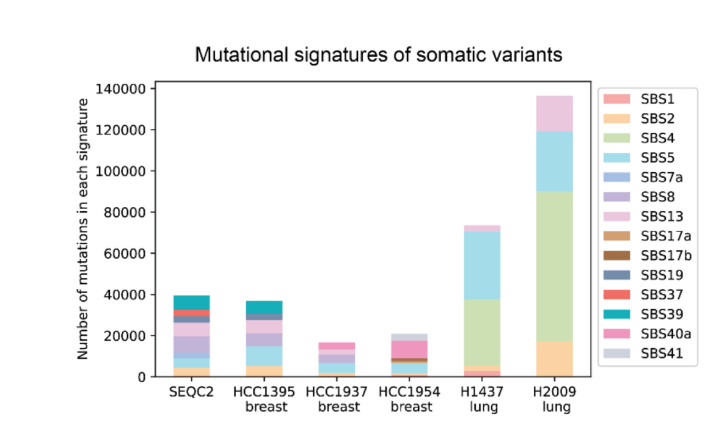
Through a convolutional neural network, DeepSomatic classifies candidate sites as either somatic variants or non-variants, ultimately generating standardized VCF or gVCF files.
Benchmark Performance
The research team trained and evaluated DeepSomatic using the CASTLE (Cancer Standard Long Read Evaluation) dataset, which includes:
- Six pairs of matched tumor and normal cell lines
- Whole-genome sequencing across three major platforms The results demonstrate significant improvements:
| Metric | DeepSomatic | Other Methods |
|---|
The team reported discovering 329,011 somatic variants, validating DeepSomatic's superior capability in insertion-deletion detection.
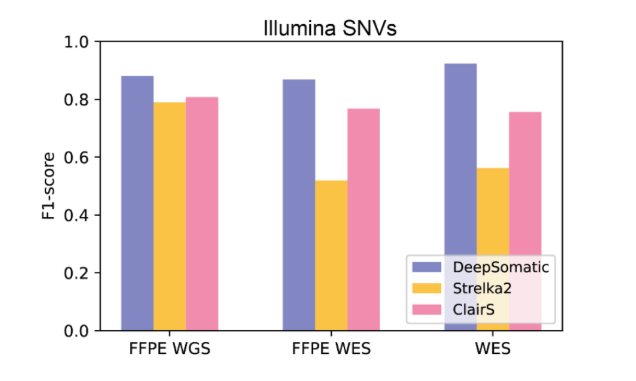
Key Advantages
The model offers several breakthroughs:
- Multi-platform support: Works across different sequencing technologies
- Adaptive tensor design: Summarizes local haplotype and error patterns effectively
- Clinical relevance: Supports tumor-normal workflows including FFPE samples
The research team has made benchmark sets publicly available to accelerate further development in cancer genomics.
Key Points
- 🌟 Detects genetic variations across multiple sequencing platforms
- 🔍 Uses CNN-powered image tensor conversion for high accuracy
- 📊 Outperforms existing methods by 10-20% in critical benchmarks