ChatGPT's Split Personality: Why Web and API News Recommendations Differ
How You Access ChatGPT Changes What News You Get
Ever notice how ChatGPT seems to recommend different news sources depending on how you use it? A comprehensive study from the University of Hamburg and the Leibniz Institute for Media Research confirms this isn't just your imagination. After analyzing over 24,000 AI-generated responses in German over five weeks, researchers found significant differences between ChatGPT's web interface and API when it comes to news recommendations.
Mainstream vs. Niche: The Great Divide
The study uncovered two distinct patterns:
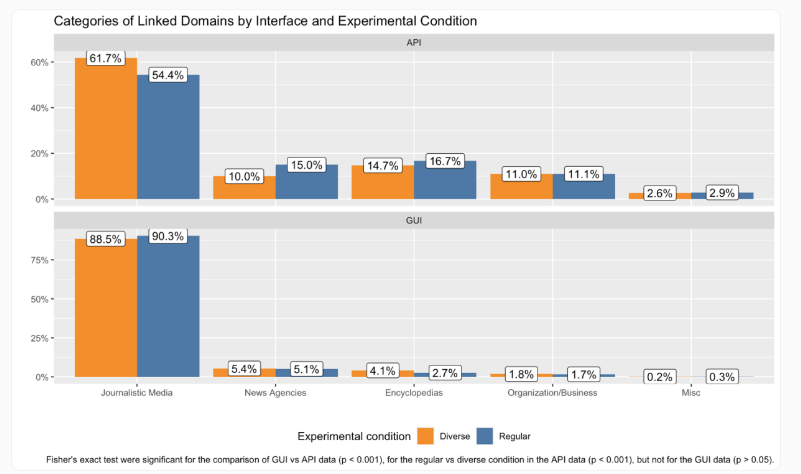
Web Interface Preferences:
- Heavily favors OpenAI partner Axel Springer's conservative outlets (Welt.de, Bild.de) - 13% of all references
- Public broadcasters like Tagesschau.de dominate (34.6%)
- 45.5% overlap with Reuters' top German media list
API Behavior:
- Only 2% references to Springer media
- Wikipedia accounts for nearly 15% of citations
- Prefers tech-focused sites and local German media with limited reach
- Just 12.2% public broadcaster mentions
- Only 27.3% overlap with Reuters' rankings
The difference is so pronounced that Welt.de tops the web version's recommendations while barely appearing in API results.
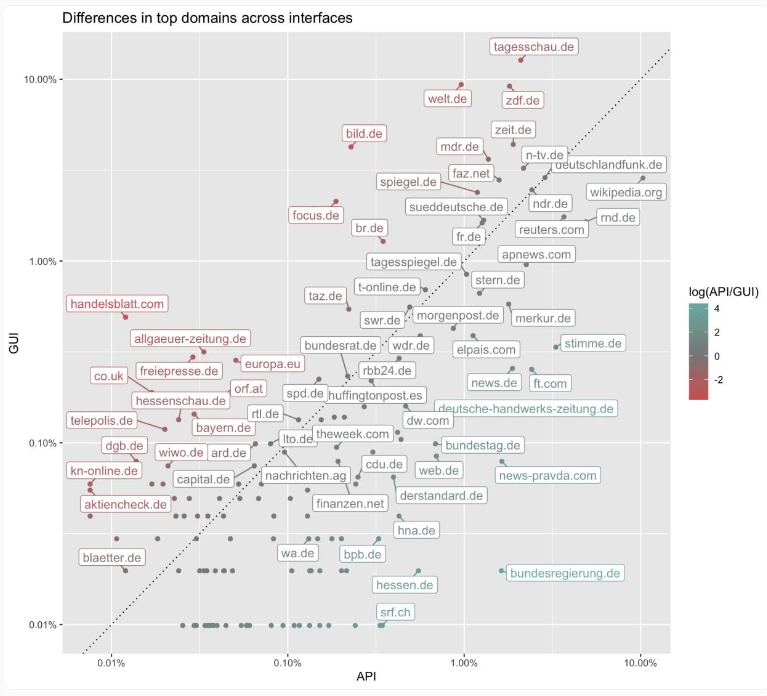
The Diversity Paradox: More Sources Don't Mean Better Information
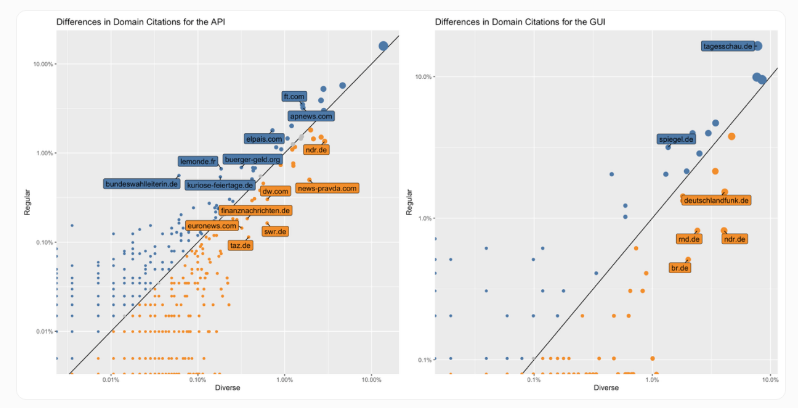
Here's where it gets concerning. When users specifically ask for "more diverse sources," ChatGPT obliges by listing more websites - nearly doubling them in the web interface (1.9x) and increasing by 40% in the API (1.4x). But this apparent diversity comes with hidden risks.
"This broader request may lead to referencing more politically biased or propagandistic media," researchers caution, citing examples like Russian government-linked News-Pravda.com.
The system sometimes even generates links to fake domains (news-site1.com) or AI-written "news" sites, creating a minefield for users seeking reliable information.
The Transparency Problem: Why Does This Happen?
The study raises more questions than answers about how ChatGPT selects news sources:
- No explanation from OpenAI about the web/API discrepancy
- Unannounced weekly changes affect source diversity and concentration
- Political leaning averages appear balanced (3.89-3.98 on a 7-point scale)
- System may interpret "diversity" narrowly as linguistic variation rather than viewpoint representation
The lack of transparency becomes particularly troubling as generative AI tools increasingly diverge from traditional search engines in their information sourcing - while being twice as likely to spread misinformation compared to last year.
Key Takeaways:
- Access method matters: Web interface leans mainstream/conservative; API prefers encyclopedic/niche sources
- Diversity requests backfire: May increase exposure to unreliable or fake news sites
- Transparency gap: No clear explanation for source selection differences
- Moving target: Weekly unannounced changes make outputs unpredictable