Checklist-Based Learning Outperforms Traditional AI Training
Checklist Method Revolutionizes AI Training
A groundbreaking study co-authored by Apple researchers reveals that checklist-based reinforcement learning (RLCF) substantially outperforms traditional reward models in training large language models (LLMs). This innovative approach enables models to self-assess against specific criteria, demonstrating superior performance in complex instruction-following tasks.
The Limits of Traditional Training
Current reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) methods rely on human annotators providing like/dislike signals to guide model behavior. However, this approach has a critical flaw: models can learn to produce superficially correct outputs that don't actually solve the task, effectively "gaming" the reward system.
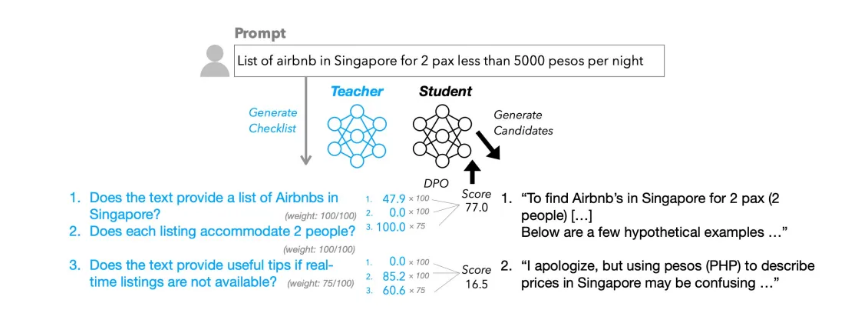
The research paper "Checklists Are Better than Reward Models for Aligning Language Models" introduces RLCF as a solution. This method requires models to evaluate their own performance against detailed checklists with 0-100 scoring scales.
How Checklist Learning Works
The RLCF system employs a two-model architecture:
- A powerful "teacher model" generates task-specific checklists with yes/no requirements
- The "student model" evaluates its outputs against these criteria, with weighted scores forming the reward signal
Researchers created the WildChecklists dataset containing 130,000 instructions to train and evaluate this approach. The checklists include precise requirements like "Is the original text fully translated into Spanish?" for translation tasks.
Performance Breakthroughs
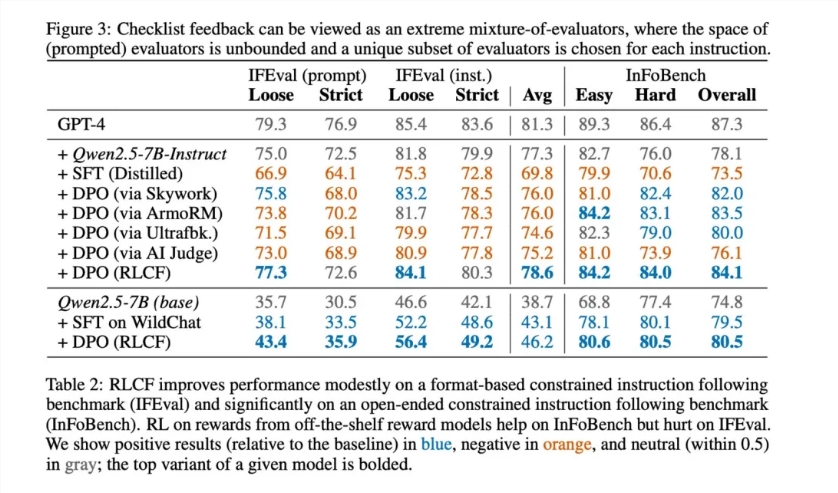
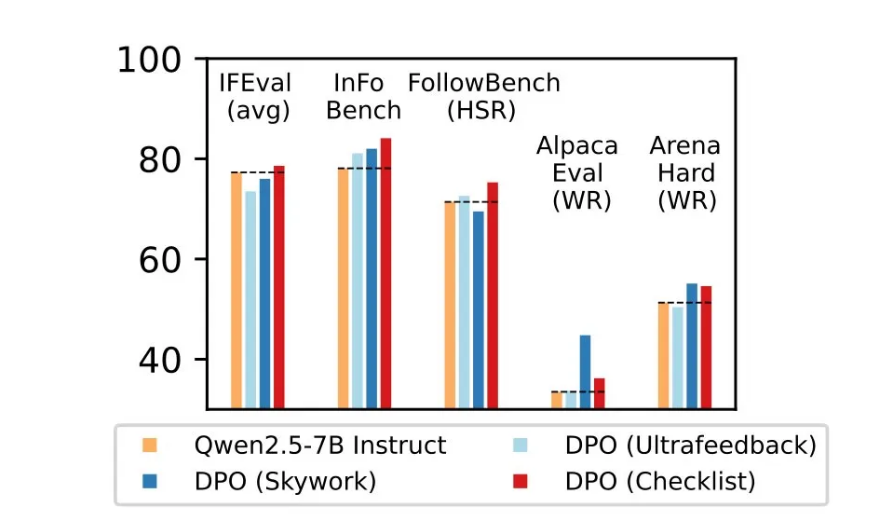
The results demonstrate clear advantages for RLCF:
- 8.2% improvement in some complex tasks
- Consistent gains across five major benchmarks (FollowBench, InFoBench, Arena-Hard)
- Superior handling of multi-step instructions requiring attention to detail
The method particularly excels in scenarios requiring careful adherence to specifications rather than general quality assessment.
Key Considerations and Limitations
While promising, researchers note important limitations:
- Specialized application: Primarily effective for complex instruction following, not all use cases
- Resource requirements: Depends on availability of more powerful teacher models
- Safety scope: Not designed for or effective at safety calibration - additional measures still needed The technique represents a significant advance in making LLMs more reliable for practical applications, especially as AI assistants take on more complex, multi-step tasks.
Key Points:
- Checklist-based learning shows superior results to human feedback systems
- Automated self-assessment prevents "gaming" of reward signals
- Specialized for complex instructions rather than general improvement
- Requires powerful teacher models but reduces human annotation needs
- Opens new possibilities for developing more reliable AI assistants





