UBTech's Thinker Model: A Game-Changer for Smarter Robots
UBTech Opens Doors With Thinker AI Model
In a significant move for robotics development, UBTech has made its Thinker artificial intelligence model publicly available. This technology aims to solve some of the most persistent challenges facing industrial humanoid robots today.
Tackling Robotics' Toughest Problems
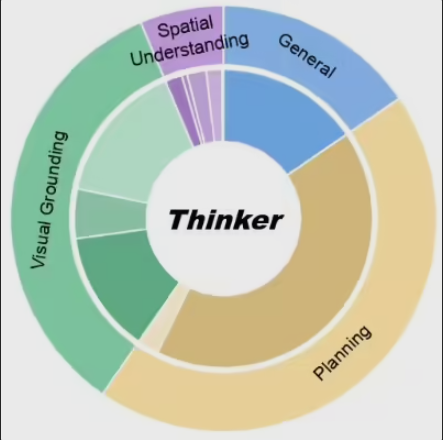
The Thinker model specifically addresses three key issues:
- Improving accuracy in spatial understanding
- Reducing excessive parameters
- Enhancing real-time performance for visual perception tasks
"Current robot models struggle with inconsistent data quality," explains a UBTech representative. "While the internet provides vast amounts of information, sorting the useful from the irrelevant remains a major hurdle."
Revolutionizing Data Processing
Thinker introduces an innovative approach to handling training data through its "refine-purify-annotate-train" cycle. The system's efficiency is remarkable - it can distill 20 billion pieces of raw data down to just 10 million high-quality samples.
The model's automated annotation system delivers even more impressive results. Combining weak supervision with self-supervision and minimal human verification, it reduces annotation costs by an astonishing 99%.

Continuous Improvement Built In
What sets Thinker apart is its ability to learn from experience. The system operates on an ongoing cycle:
- Annotation
- Training
- Feedback
- Iteration
This process allows for constant refinement of accuracy, moving steadily toward truly intelligent robotic operations.
Opening Doors for Innovation
By making Thinker open-source, UBTech invites developers worldwide to build upon their work. Researchers can now access this powerful "brain" for robots, potentially accelerating progress in embodied intelligence technologies.
The company's decision reflects confidence in their technology while demonstrating commitment to advancing the entire robotics field. As one industry analyst noted: "This could be the spark that ignites the next wave of robotic innovation."
Key Points:
- Data efficiency: Processes 20B raw inputs → 10M quality outputs
- Cost savings: Reduces annotation expenses by 99%
- Continuous learning: Self-improving through feedback loops
- Open access: Available to all developers for research and applications