Northeastern University's Translation Model Bridges Global Language Gaps
Northeastern University Breaks New Ground in Multilingual AI Translation
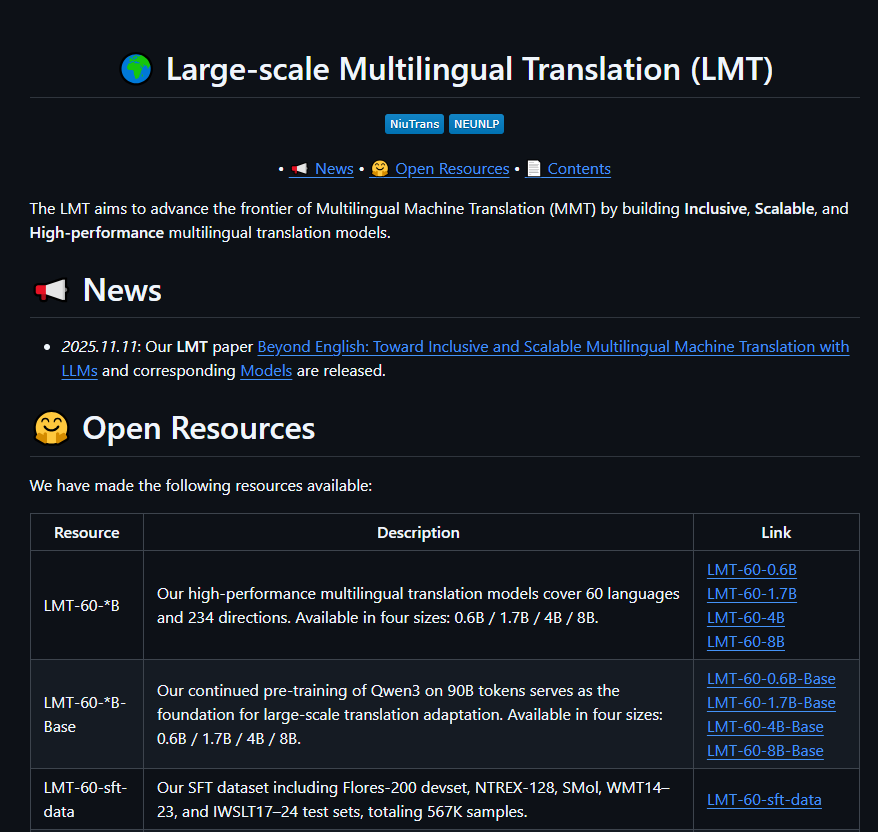
The world just became a little smaller thanks to Northeastern University's latest breakthrough. Their NiuTrans.LMT translation model now bridges 60 languages across an impressive 234 translation directions - and it's doing so while challenging traditional approaches.
Rethinking Translation Architecture
Most translation models route everything through English, creating what researchers call "meaning potholes" - places where nuance gets lost in multiple translations. NiuTrans.LMT takes a different path with its Chinese-English dual-center design. This means cleaner translations between Chinese and 58 other languages, plus English and 59 others.
"Imagine trying to explain a Tibetan poem to someone in Ethiopia," says lead researcher Dr. Li Wei. "Previously, that might go Tibetan→English→Amharic with meaning leaking at each step. Now it's direct."
Bringing Marginalized Languages Into the Digital Age
The team categorized languages into three tiers:
- 13 high-resource languages (French, Arabic, etc.): Human-level fluency
- 18 medium-resource languages (Hindi, Finnish): Strong technical accuracy
- 29 low-resource languages (Tibetan, Swahili): Now moving from "untranslatable" to practical use
The model achieved this through innovative training:
- Continued pre-training: Balanced learning across 90 billion multilingual tokens
- Supervised fine-tuning: Refined using premium parallel texts covering 117 directions
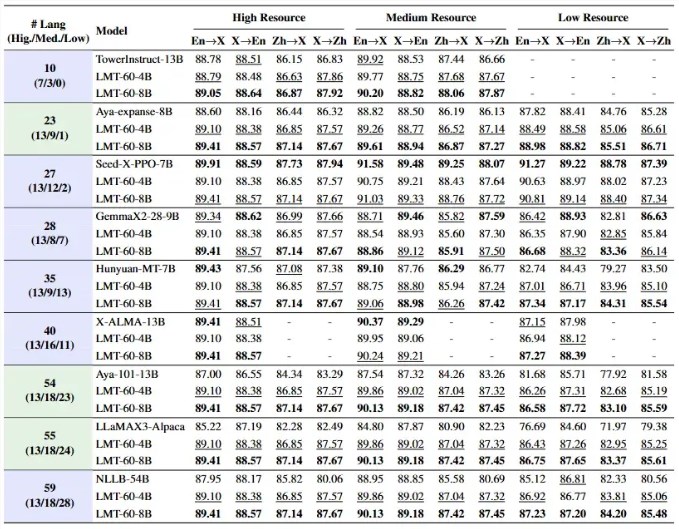
The results? Top rankings on the FLORES-200 benchmark among open-source models.
Scalable Solutions for Every Need
Understanding that one size doesn't fit all, the team released four versions:
| Version | Best For |
|---|
All versions are available free on GitHub and Hugging Face.
More Than Technology - A Cultural Bridge
This isn't just about bits and algorithms. When an Ethiopian farmer can read Tibetan poetry accurately translated, or Nordic scholars can study Swahili proverbs without distortion, we're preserving cultural heritage digitally.
The project represents Northeastern University's commitment to what Dr. Li calls "technological democracy" - making advanced AI accessible globally rather than keeping it locked in tech hubs.
Key Points:
- Supports direct translation between Chinese/English and 58/59 other languages respectively
- Special focus on previously underserved languages like Tibetan and Amharic
- Four scalable versions available open-source
- Outperforms competitors on FLORES-200 benchmark
- Represents significant progress toward global language equality

