Ant Group and Renmin University Unveil First Native MoE Diffusion Language Model
Ant Group and Renmin University Unveil Groundbreaking LLaDA-MoE Model
At the 2025 Inclusion·Bund Conference, Ant Group and Renmin University jointly introduced LLaDA-MoE, the industry's first native Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture diffusion language model (dLLM). This breakthrough challenges the conventional belief that language models must be autoregressive.
Key Innovations
The LLaDA-MoE model was trained from scratch on approximately 20 terabytes of data, demonstrating remarkable scalability and stability in industrial-scale training. It outperforms previous dense diffusion language models like LLaDA1.0/1.5 and Dream-7B, while matching the performance of equivalent autoregressive models like Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct. Notably, it achieves this by activating only 1.4 billion parameters out of a total 7 billion.

Caption: Renmin University and Ant Group jointly launched the first MoE architecture diffusion model LLaDA-MoE.
Performance Highlights
Under Ant's unified evaluation framework, LLaDA-MoE showed an average improvement of 8.4% across 17 benchmarks, including HumanEval, MBPP, and GSM8K. It leads LLaDA-1.5 by 13.2% and ties with Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct, validating the "MoE amplifier" effect in the dLLM field.
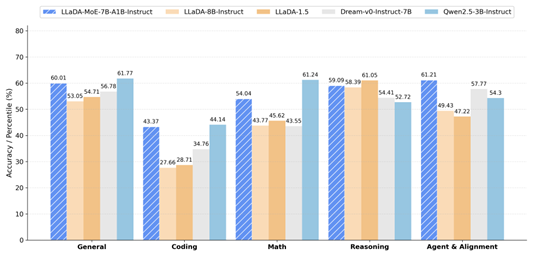
Caption: Performance metrics of LLaDA-MoE compared to other models.
Technical Breakthroughs
Lan Zhenzhong, Director of Ant Group's General AI Research Center, emphasized that this model represents a significant step toward scaling dLLMs to larger sizes. The team rewrote training code based on LLaDA-1.0 and utilized Ant's distributed framework ATorch for parallel acceleration.
Assistant Professor Li Chongxuan from Renmin University highlighted that traditional autoregressive models struggle with bidirectional token dependencies, a limitation addressed by LLaDA-MoE's parallel decoding approach.
Open-Source Commitment
Ant Group plans to open-source not only the model weights but also a custom inference engine optimized for dLLM parallelism, which reportedly outperforms NVIDIA's fast-dLLM solution. Technical reports and code will be released on GitHub and Hugging Face.
Key Points:
- First native MoE architecture diffusion language model (dLLM)
- Trained on 20T data with 7B total parameters (1.4B activated)
- Outperforms dense diffusion models; matches autoregressive counterparts
- Open-sourcing model weights and inference framework soon



