OLMo 2 32B: Open-Source AI Model Challenges GPT-3.5 Turbo
The Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence (AI2) has unveiled OLMo 2 32B, a groundbreaking open-source large language model (LLM) that challenges the dominance of proprietary models like GPT-3.5 Turbo. With 32 billion parameters, OLMo 2 32B not only matches but surpasses its competitors in several academic benchmarks, marking a significant milestone in the democratization of AI.
A Fully Open-Source Model
One of the most notable features of OLMo 2 32B is its complete transparency. AI2 has released all associated data, code, weights, and detailed training processes, setting a new standard for openness in AI development. This stands in stark contrast to the closed-door policies of many proprietary models, which often withhold critical details.
AI2's decision to make OLMo 2 32B fully open-source aims to foster global collaboration and innovation. By providing researchers with access to the model's inner workings, the institute hopes to accelerate advancements in the field and demonstrate that high-performance AI can be developed without secrecy.
Performance That Rivals Proprietary Models
OLMo 2 32B's 32 billion parameters represent a significant scale-up from its predecessors, enabling it to achieve remarkable performance. In benchmark tests, it has outperformed both GPT-3.5 Turbo and GPT-4o mini, proving that open-source models can compete with those developed by well-funded organizations.
The model's success is attributed to its refined training process, which is divided into two main stages: pre-training and mid-training. During pre-training, OLMo 2 32B processed an extensive dataset of approximately 3.9 trillion tokens from diverse sources, including DCLM, Dolma, Starcoder, and Proof Pile II. This phase provided the model with a broad foundation of knowledge.
Mid-training focused on the Dolmino dataset, a high-quality collection of 843 billion tokens covering educational, mathematical, and academic content. This targeted approach enhanced the model's understanding in specialized domains, ensuring robust and nuanced language capabilities.
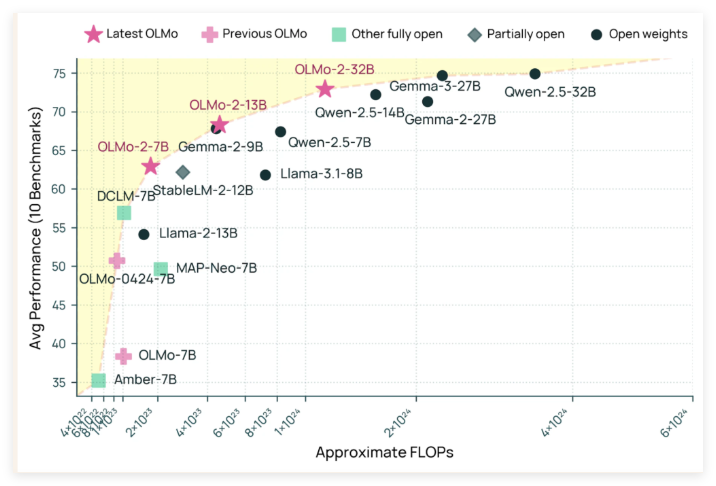
Efficiency in Training and Resource Use
Beyond its superior performance, OLMo 2 32B demonstrates exceptional training efficiency. It achieves results comparable to leading open-weight models while using only about one-third of the computational resources required by models like Qwen2.532B. This efficiency underscores AI2's commitment to developing resource-conscious AI solutions.
The implications of this efficiency are profound. By reducing the computational burden, OLMo 2 32B makes advanced AI more accessible to researchers and developers with limited resources. This could pave the way for more inclusive innovation in the field.
A Milestone for Open AI Development
The release of OLMo 2 32B represents more than just a new model; it signifies a shift toward open and accessible AI development. By offering a high-performance alternative to proprietary models, AI2 challenges the notion that only large corporations can lead in AI innovation.
The model's success also highlights the importance of meticulous design and efficient training methods. As more researchers build upon OLMo 2 32B's foundation, the potential for breakthroughs in artificial intelligence grows exponentially.
Looking Ahead
The introduction of OLMo 2 32B is expected to invigorate AI research by lowering barriers to entry and promoting collaboration. For organizations clinging to proprietary models, this development serves as a reminder that openness may be key to long-term success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Key Points
- OLMo 2 32B is a fully open-source LLM with 32 billion parameters, developed by the Allen Institute for AI.
- It outperforms GPT-3.5 Turbo and GPT-4o mini in benchmark tests.
- The model was trained on diverse datasets totaling nearly 4 trillion tokens, with a focus on specialized domains during mid-training.
- OLMo 2 32B achieves high performance using significantly fewer computational resources than comparable models.
- Its release marks a major step toward democratizing access to advanced AI technologies.



