Google Launches Chrome DevTools MCP Beta for AI Browser Control
Google Launches Public Beta of Chrome DevTools MCP
Google has unveiled the public beta of Chrome DevTools MCP, a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server designed to empower AI coding agents with real-time browser control. This tool enables AI agents to inspect and manipulate live Chrome instances, addressing a critical limitation in current code-generation systems.
What is Chrome DevTools MCP?
The MCP is an open protocol that connects large language models (LLMs) with development tools and runtime data. Google's implementation serves as a dedicated server, exposing Chrome's debugging interface to MCP-compatible clients. As described in Google's developer blog, this brings "the power of Chrome DevTools to AI coding assistants," creating a closed-loop system where agents can test and refine their suggestions against actual browser behavior.
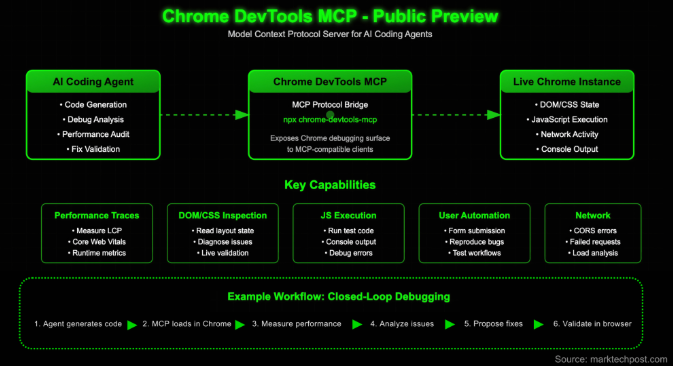
Key Features and Capabilities
The GitHub repository outlines extensive functionality including:
- Performance tracking: Agents can initiate traces (
performance_start_trace) and analyze results to suggest optimizations - Navigation controls: Commands like
navigate_page,new_page, andwait_forenable page flow automation - User input simulation: Supports actions like
click,fill,drag, andhover - Runtime inspection: Tools for checking console messages (
list_console_messages), evaluating scripts (evaluate_script), and monitoring network requests (get_network_request) - Visual verification: Screenshot and DOM snapshot capabilities support visual regression testing
The system leverages Puppeteer for reliable automation while communicating through the standard Chrome DevTools Protocol (CDP).
Installation and Integration
Setting up an MCP client requires minimal configuration:
json
{
"mcpServers": {
"chrome-devtools": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["chrome-devtools-mcp@latest"]
}
}
}
The server integrates with popular development tools including:
- Gemini CLI
- Claude Code
- Cursor IDE
- GitHub Copilot (via
code --add-mcpcommand)
The package requires Node.js ≥22 and current Chrome versions.
Practical Applications
Google demonstrates several use cases where this technology shines:
- Real-time debugging: Agents can verify suggested fixes against actual browser behavior rather than static analysis
- Network troubleshooting: Identifying CORS issues or blocked resource requests through direct inspection
- User flow validation: Simulating form submissions to reproduce reported errors
- Layout analysis: Reading DOM/CSS context to diagnose rendering issues
- Performance optimization: Running automated audits to reduce metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) github: https://github.com/ChromeDevTools/chrome-devtools-mcp |
|# Key Points | *Real-time Control: Enables AI agents to interact with live browsers | *Comprehensive Tooling: Supports performance analysis, user simulation, and runtime inspection | *Seamless Integration: Easy setup process works with major development environments |