AI Chatbots Lose 39% Accuracy in Long Conversations, Microsoft Study Finds
A groundbreaking study by Microsoft and Salesforce has exposed a critical weakness in today's most advanced AI language models: their ability to maintain accuracy crumbles during prolonged conversations. The research shows system performance drops by an alarming 39% when users progressively clarify their needs through multiple exchanges.
Testing Reveals Startling Performance Gaps
The research team developed an innovative "sharding" testing method that mimics real-world conversations where users gradually refine their requests. Unlike traditional single-prompt evaluations, this approach breaks tasks into sequential steps - mirroring how people actually interact with AI assistants.
Results shocked researchers. Model accuracy plunged from approximately 90% to just 51% across all tested systems. This decline affected every model evaluated, from compact open-source options like Llama-3.1-8B to industry-leading commercial systems such as GPT-4o.
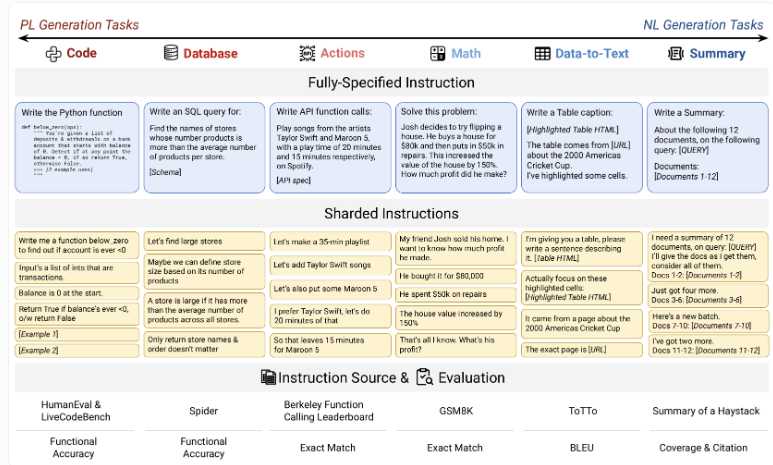
Each test involved 90-120 instructions decomposed into subtasks using high-quality datasets, creating rigorous evaluation conditions.
Even Top Performers Struggle
The study's highest-rated models - Claude3.7Sonnet, Gemini2.5Pro, and GPT-4.1 - all showed concerning drops of 30-40% in multi-round dialogues compared to single interactions. More troubling was their wild inconsistency, with performance varying up to 50 points on identical tasks.
Four Critical Failure Modes Identified
Researchers pinpointed four fundamental problems plaguing AI models in extended conversations:
- Rushed Judgments: Models frequently reach conclusions before gathering complete information
- Historical Bias: Overdependence on earlier responses, even when clearly incorrect
- Selective Attention: Critical details get overlooked as conversations progress
- Verbal Overload: Excessive detail creates confusion about missing information
Technical Fixes Fall Short
The team attempted multiple technical solutions:
- Reducing model "temperature" to decrease randomness
- Having AI repeat instructions for clarity
- Adjusting information density at each step
None produced meaningful improvements. The only reliable workaround? Providing all necessary details upfront - a solution that defeats the purpose of conversational AI.
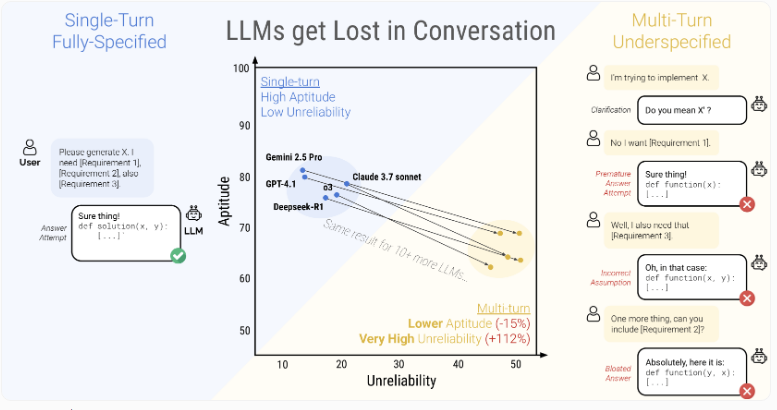
The study reveals large language models often "lose the thread" in multi-step dialogues, leading to dramatic performance declines.
Capability vs. Reliability Divide
The data shows two distinct failure layers: a modest 16% drop in basic capability but a staggering 112% increase in unreliability. While more capable models typically perform better on single tasks, all models regress to similar poor performance in extended conversations regardless of their baseline abilities.
Practical Recommendations Emerge
The findings suggest concrete strategies: For Users:
- Restart conversations when they veer off track rather than attempting corrections
- Request end-of-chat summaries to use as fresh starting points For Developers:
- Prioritize reliability in multi-turn dialogue systems
- Build models that handle incomplete instructions natively without prompt engineering tricks
The implications are profound for an industry racing to deploy AI assistants across customer service, healthcare, and education. As one researcher noted: "Reliability isn't just another metric - it's the foundation determining whether these systems deliver real value or just create frustration." Key Points
- AI models show 39% lower accuracy in progressive conversations versus single interactions
- All tested systems - including top commercial models - exhibited similar reliability failures
- Four core issues cause breakdowns: premature conclusions, history overreliance, information neglect, and excessive detail
- Technical optimizations proved ineffective; complete upfront information remains the only reliable solution
- The findings highlight critical challenges for real-world AI assistant deployment




